Exploring the Role of Traditional Chinese Medicine in Combating Antibiotic Resistance
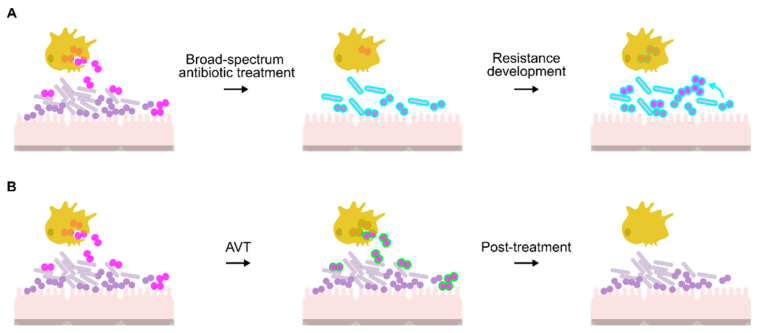
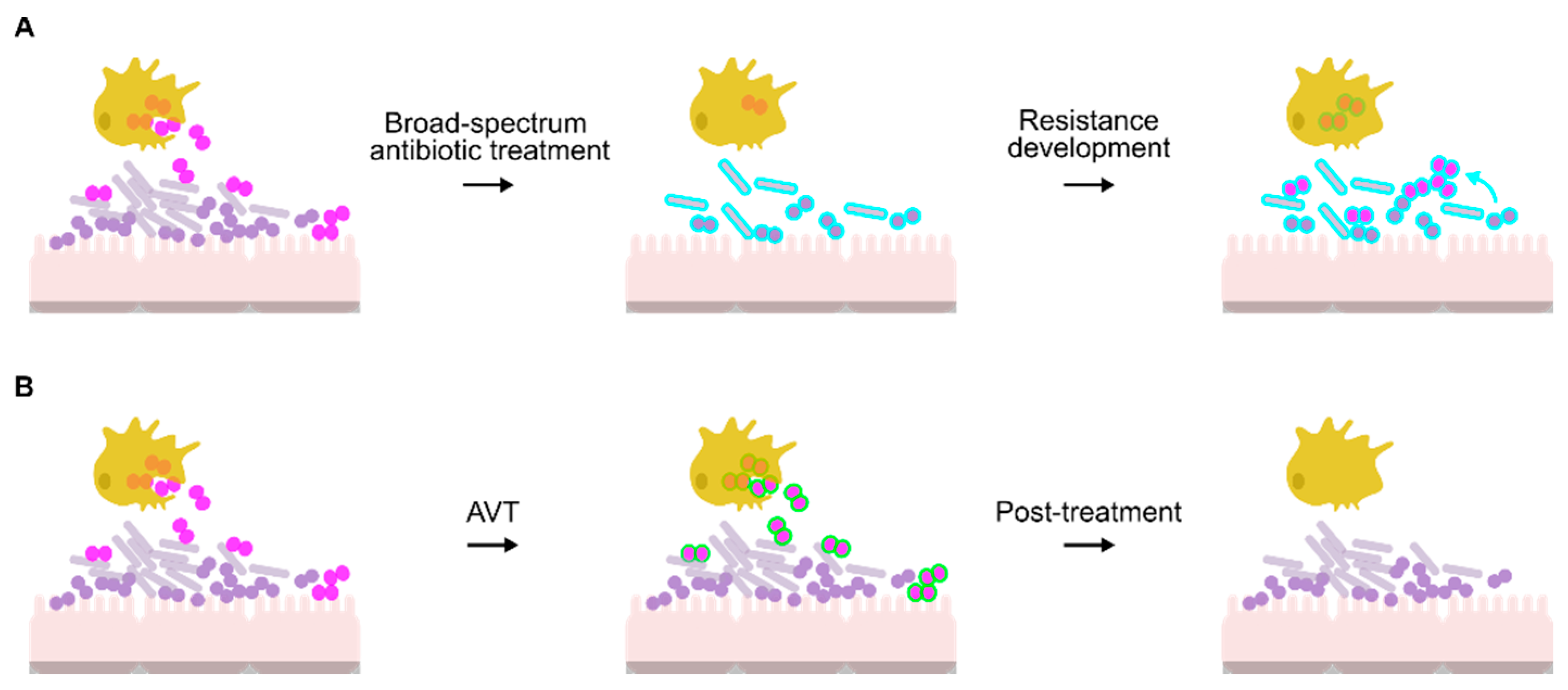
Gonorrhea remains one of the most challenging infectious diseases affecting global public health, with over 82 million new cases reported among adults worldwide in 2020. As the conventional treatment—ceftriaxone monotherapy—faces increasing vulnerability due to rising antimicrobial resistance, the need to seek out innovative and alternative treatment strategies has never been more essential. This opinion editorial aims to take a closer look at a recent study that explored the antibacterial properties of 13 traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) formulations against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, offering insights into potential new directions in the fight against drug-resistant infections.
The study under discussion presents an intriguing intersection between ancient medical practices and modern scientific methodologies. In a time when modern medicine continuously battles against the tangled issues of antibiotic resistance, the findings about TCM reflect not only hope for alternative therapies but also highlight the nerve-racking twists and turns faced when trying to manage our dependence on conventional antibiotics.
Assessing the Current Landscape of Antibiotic Resistance in Gonorrhea
The global burden of gonorrhea is daunting, with the infection contributing to severe health implications, including infertility and an increased risk of HIV transmission. Given the escalating resistance to standard treatments, it is clear that fighting back against Neisseria gonorrhoeae requires exploring all possible treatment avenues. Although modern medicine has advanced significantly, the tricky parts of antibiotic resistance remind us that innovation is a must-have in our therapeutic arsenal.
While many initiatives have attempted to combat antibiotic resistance, the research into alternative agents has not been as widespread. Antibiotic resistance is a full of problems issue: bacteria evolve rapidly, and the subtle parts of drug efficacy can be easily overshadowed by emerging resistant strains. Consequently, researchers have been driven to consider the potential of traditional medicine, looking at centuries-old remedies that have been largely tested on different conditions.
Exploring Natural Products Against Drug-Resistant Infections
One of the most promising areas of emerging research is the investigation of natural products and their ability to fight bacterial infections resistant to standard treatments. Traditional Chinese Medicine, with its storied history and holistic approach, offers a wide array of herbal preparations that have been used for centuries. The recent study examined 13 such traditional formulations using rigorous scientific protocols, including the agar dilution method, to measure the minimum inhibitory concentrations (MICs) that prevent bacteria from growing.
By getting into the details of how these TCM formulations perform against Neisseria gonorrhoeae, researchers hope to provide a viable alternative or supplementary treatment to classical antibiotics. This commitment to digging into natural remedies reflects an awareness that nature often holds key answers to some of the most complicated pieces of modern medicine’s challenges.
Investigating the Tricky Parts of Antibacterial Testing Using Agar Dilution
Testing the antibacterial activity of any compound against a resistant pathogen involves navigating several confusing bits of methodology. In this study, the research team applied the agar dilution method to evaluate the MICs of each TCM on 280 clinical isolates of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. This approach, although off-putting to many due to its nerve-racking precision and detailed execution, provides a reliable measure of how effective a substance is in stopping bacterial growth.
The process is straightforward in concept yet can be riddled with tension during its laboratory execution. The method involves incorporating different concentrations of the active agents into an agar medium, inoculating the bacteria, and then determining the lowest concentration at which the bacteria do not grow. Such experiments do more than just offer simple numbers; they provide a blueprint of the promising and challenging parts of each TCM’s antibacterial efficacy.
Key Methodological Considerations
- Standardization: Ensuring that each TCM formulation is prepared and applied consistently is fundamental to obtain any meaningful comparison with standard antibiotics.
- Reproducibility: The agar dilution method must be carried out with strict adherence to protocols to minimize the confusing bits that might arise from experimental variations.
- Correlation Analysis: Comparing the MICs of TCM agents with those of established antibiotics like ceftriaxone, spectinomycin, and azithromycin helps researchers tease out potential cross-resistance issues.
These points serve as a concise guide to understanding why each step—though seemingly straightforward—requires meticulous attention, and why the method ends up being key to unlocking the hidden complexities of antibacterial action in natural products.
Dissecting the Promising Findings: The Case of Coptidis Rhizoma and Others
Among the 13 TCM formulations studied, Coptidis Rhizoma (CR) stood out with the lowest MIC values, indicating a particularly effective antibacterial activity against Neisseria gonorrhoeae. The MIC10 for CR was reported to be ≤0.06 mg/mL, and the MIC90 was ≤0.5 mg/mL—figures that suggest considerable potential in halting the growth of even resistant bacterial strains.
This promising observation opens the door to various exciting possibilities in treating gonorrhea, especially as researchers continue to look for alternatives to conventional antibiotics. Besides CR, other formulations such as Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (PCC), Forsythiae Fructus (FF), Taraxaci Herba (TH), and Scutellariae Radix (SR) also demonstrated significant antibacterial effects.
Summary Table of TCM Efficacy
| TCM Formulation | MIC10 (mg/mL) | MIC90 (mg/mL) | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coptidis Rhizoma (CR) | ≤0.06 | ≤0.5 | Strong antibacterial activity |
| Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex (PCC) | Not specified | Significant reduction in bacterial growth | Promising alternative agent |
| Forsythiae Fructus (FF) | Not specified | Effective in several isolates | Potential for integration in treatment |
| Taraxaci Herba (TH) | Not specified | Good antibacterial performance | Requires further research |
| Scutellariae Radix (SR) | Not specified | Effective against resistant strains | Highlights therapeutic promise |
These findings give us a clear picture of which TCM formulations might be most effective and point out the nerve-racking yet essential need to distinguish between agents with true promise and others that may carry hidden challenges.
Understanding the Chemical Profiles: GC-MS and LC-MS/MS Analysis
Beyond simply documenting antibacterial activity, the study employed advanced techniques such as Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) to poke around the chemical profiles of the TCM formulations. These methods help in identifying the specific chemical components responsible for the observed antibacterial effects.
Diving in to understand these chemical profiles is not an easy task, as the fine points of natural formulations can be as tangled as a bowl of mixed ingredients. However, such detailed analysis is essential to determine which metabolites or chemical structures are the driving forces behind the antibacterial actions against Neisseria gonorrhoeae.
The Importance of Chemical Characterization
- Identifying Active Constituents: Recognizing the specific chemical compounds in each formulation helps researchers figure a path toward isolating potent antibacterial agents.
- Ensuring Consistency: For a natural remedy to be considered as an alternative treatment, its chemical composition must be consistent, ensuring that results are reproducible in clinical settings.
- Potential for Synthesis: Once active compounds are identified, there is the possibility of synthesizing them or enhancing their efficacy through pharmaceutical modifications.
These critical steps in chemical analysis not only validate the observed antibacterial properties but also lay the foundation for translating ancient remedies into modern treatments, overcoming some of the tricky parts that often complicate the integration of TCM into contemporary medical practice.
Addressing the Cross-Resistance Conundrum
One of the most challenging and charged issues in oncology and antibiotic research is the phenomenon of cross-resistance. The study revealed that while many TCM formulations exhibited good antibacterial activity independent of traditional antibiotics, some—specifically Bupleuri Radix (BR) and Cimicifugae Rhizoma (CFR)—showed a correlation with the MIC values of ceftriaxone, azithromycin, and spectinomycin.
This observed correlation raises concerns about the potential for overlapping mechanisms of resistance, suggesting that not all TCM formulations are suitable as stand-alone alternatives. For these particular agents, there might be a risk that using them could inadvertently encourage cross-resistance between traditional remedies and conventional antibiotics. Thus, while some TCMs show considerable promise, others carry pitfalls that require careful, methodical evaluation.
Considerations to Keep in Mind
- Risk of Cross-Resistance: The presence of chemical similarities between some TCM formulations and conventional antibiotics might lead to shared resistance mechanisms.
- Need for Combination Therapies: Agents with potential cross-resistance issues might require combination with other treatments to reduce the risk of resistance development.
- Further Research: Additional in vitro and in vivo experiments are essential to better understand the clinical implications of these correlations.
Facing the tangled issues of cross-resistance means that, much like in any scientific investigation, one must carefully balance the promise of natural products with the need for rigorous testing and validation. It is a reminder that while nature offers many potential cures, the path to their successful integration into modern medicine is loaded with challenges.
Integrative Medicine: Merging TCM and Conventional Therapeutics
The exploration of TCM for treating infections like gonorrhea opens a broader dialogue about integrative medicine, where traditional therapies are not seen in opposition to conventional medicine but rather as potential complements. Integrative medicine encourages a mixed approach—using the strengths of both modern pharmacology and ancient therapeutic wisdom—to tackle conditions that are full of problems and ever-evolving bacterial resistance.
In practical terms, this means that rather than replacing existing antibiotic treatments, effective TCM formulations might serve to reinforce them. Combined therapy could potentially reduce the doses required of conventional antibiotics and diminish the nerve-racking side effects or the risk of developing further resistance.
Potential Benefits of an Integrated Approach
- Enhanced Efficacy: Using TCM alongside standard antibiotics may produce a synergistic effect, thereby boosting overall antibacterial efficacy.
- Reduction in Resistance Development: A combined treatment regimen may lessen the bacteria’s ability to develop resistance against any single agent.
- Holistic Healing: Integrative approaches often focus on restoring overall health and balance, which can be particularly beneficial in managing complex infections.
- Personalized Medicine: With varied responses to treatments, integrative approaches allow for a more customized therapeutic strategy based on patient history and the specific bacterial profile.
This balanced approach may also offer a way to work through the challenging parts of antibiotic use in a manner that respects the nuanced ways in which bacteria adapt and evolve. By taking advantage of the strengths of both traditional and modern treatments, clinicians may find new paths through the maze of antibiotic resistance.
Discussing the Societal and Economic Implications
Beyond the laboratory and clinical implications, the shift toward integrating TCM in the treatment of drug-resistant gonorrhea carries substantial societal and economic implications. In many parts of the world, traditional remedies are more accessible and affordable compared to high-cost, modern antibiotics. This accessibility can be a key factor in managing public health, especially in areas that struggle with the economic challenges of healthcare.
Moreover, the potential to reduce healthcare costs by incorporating effective TCM treatments is an important conversation. In nations where medical resources are on edge, the availability of alternative, natural remedies might relieve some of the pressure on the healthcare system. However, balancing such cost-effective strategies with robust scientific validation is a tricky matter that requires careful policy planning and sustainable investment.
Key Points on Societal Impact
- Accessibility: TCM formulations are often based on naturally sourced ingredients, which can be locally available and less expensive.
- Economic Relief: Reducing the dependency on high-cost antibiotics could lower overall healthcare expenditures.
- Health Equity: Alternative treatments might offer more equitable healthcare solutions, particularly in under-resourced regions.
- Cultural Integration: Embracing TCM supports cultural heritage and knowledge, fostering respect for traditional practices in modern societies.
The emphasis on community-driven health solutions is critical, especially in an era when healthcare systems are trying to find their way around a maze of emerging trends and budget constraints. This dialogue encourages a rethinking of how we deliver healthcare, segueing into a broader movement toward integrative medicine that respects both ancient wisdom and modern science.
Future Perspectives and the Road Ahead
Despite the promising results of exploring TCM’s antibacterial activity, experts agree that additional research is essential. The study in discussion is a foundational step, but clinical validation remains necessary to truly incorporate these natural formulations into standard practice.
Looking ahead, there are several key areas where future research and policy planning can focus. First, more extensive in vitro studies need to be conducted to confirm the initial promising outcomes. Then, carefully designed clinical trials will be crucial to determine the safety, dosage, and overall therapeutic efficacy of these TCM agents in real-world settings. Finally, interdisciplinary collaboration between modern pharmacologists, traditional medicine practitioners, and policymakers could pave the way for novel, integrated treatment regimens that are tailored to current medical needs.
Essential Future Directions
- Clinical Trials: Large-scale studies will allow us to confirm whether the promising MIC values observed in the lab translate into effective human treatments.
- Standardized Formulations: Developing standardized extracts and formulations of TCM ingredients is super important to ensure consistent efficacy and safety.
- Mechanistic Studies: A deeper investigation into the specific biochemical mechanisms of TCM compounds will help in understanding how these agents interact with bacterial cells, particularly in the presence of existing antibiotics.
- Policy and Regulation: Integrating TCM into conventional medical systems requires updated regulatory frameworks that address quality control, dosage standards, and safety testing.
With these focused research directions, there is hope that TCM can eventually play a role in easing the overwhelming pressure modern medicine faces in dealing with antibiotic resistance. The path forward, though packed with complicated pieces and nerve-racking decisions, appears promising with a collaborative and integrative framework.
Clinician and Patient Considerations in Integrative Therapies
As we look to the future, it is critical to recognize the roles of both clinicians and patients in this evolving medical landscape. For health practitioners, the adoption of integrative therapies that combine TCM with conventional antibiotics means continuously updating their understanding of both fields. They must find a way to figure a path through the maze of clinical challenges while remaining open-minded about alternative approaches. This requires training, evidence-based guidelines, and an ongoing commitment to patient safety.
Patients, on their end, need clear guidance on the benefits and potential pitfalls of such integrated approaches. Educational initiatives that explain the small distinctions between various treatment options can help demystify traditional remedies and empower patients to take an active role in their healthcare decisions.
Recommendations for Clinicians and Patients
- Clinician Education: Regular training sessions and updates on the latest advances in both conventional and traditional therapies can help bridge the knowledge gap.
- Patient Information: Accessible literature that breaks down the fine shades of each treatment option—including benefits and risks—will empower patients to make informed decisions.
- Collaborative Care: A team-based approach, involving experts in both modern pharmacology and traditional medicine, can provide more holistic care and support.
- Feedback Mechanisms: Establishing channels for patient feedback and real-world reports on treatment outcomes is key to refining integrative practices on the fly.
This approach not only eases the nerve-racking aspects of adopting new therapies but also builds trust between practitioners and patients. When both parties work together to tackle the overwhelming issues of antibiotic resistance, the chances of success are significantly increased.
Balancing Optimism with Caution in the Era of Alternative Therapies
One of the most compelling aspects of this study is its potential to redefine how we approach bacterial infections that have become increasingly resistant to conventional treatments. Yet, amid the optimism, it is crucial to proceed with a measure of cautious pragmatism. While formulations like Coptidis Rhizoma and others show considerable promise, it would be impractical to assume that they will serve as a silver bullet against drug-resistant bacteria without comprehensive clinical validation.
The interplay of natural compounds with existing drugs may sometimes lead to unexpected results, making it essential to evaluate them through comprehensive studies. Researchers and clinicians alike need to work through the tricky parts of potential side effects, dosing challenges, and the possibility of cross-reactions, especially when combining modern and traditional medications.
This balancing act calls for continued research and open dialogue among scientists, clinicians, and the broader medical community. Such discussions must openly address both the exciting possibilities and the lingering questions that arise when conventional approaches meet alternative therapies.
Points of Caution
- Rigorous Testing: Every promising natural remedy must undergo methodical clinical trials before it can be recommended for mainstream use.
- Monitoring for Adverse Effects: Detailed monitoring is required to identify and manage any potential side effects that may emerge during combined treatments.
- Understanding Interactions: It is essential to explore how these natural products interact with standard antibiotics to prevent any inadvertent development of cross-resistance.
- Transparency in Research: Open sharing of data and continuous peer review will be key components in ensuring that any integrative approach is scientifically sound.
By acknowledging these points of caution, the medical community can innovate without losing sight of patient safety and overall therapeutic efficacy. The journey to shifting paradigms in treating gonorrhea is intricate, but with a balanced approach, the fine points of each step can be managed successfully.
Conclusion: Charting a New Course in the Fight Against Gonorrhea
The battle against gonorrhea—a disease that imposes significant health and economic burdens worldwide—is at a critical juncture. With traditional treatment options facing growing resistance, the exploration of alternative remedies such as traditional Chinese medicine offers a promising supplemental strategy. Even though there are nerve-racking challenges and complicated pieces in integrating natural products with conventional therapies, emerging research like the study discussed here demonstrates potential paths that can be taken.
From meticulously measuring antibacterial activity using the agar dilution method to diving in on chemical characterizations with GC-MS and LC-MS/MS, the study provides a comprehensive look at how ancient remedies stand up to modern scientific scrutiny. The encouraging results for formulations such as Coptidis Rhizoma, Phellodendri Chinensis Cortex, Forsythiae Fructus, Taraxaci Herba, and Scutellariae Radix give us practical starting points for a more integrated approach to treating gonorrhea.
At the same time, the research warns us not to overlook the potential for cross-resistance, as seen with Bupleuri Radix and Cimicifugae Rhizoma. These insights are a timely reminder that while integrating TCM into contemporary antibiotic regimens has considerable promise, it also carries hidden challenges and subtle details that must be addressed by further studies and clinical trials.
By working together—clinicians, researchers, and policymakers—we can figure a path through the tricky parts of antibiotic resistance and harness the best of both modern and traditional therapies. As we move forward, balanced discussion, rigorous testing, and mindful integration will be the cornerstones of a healthcare landscape that is better equipped to handle both the overwhelming and the complicated pieces of modern medicine’s challenges.
Ultimately, the potential integration of TCM into mainstream treatment regimens stands as a testament to the power of combining time-honored wisdom with cutting-edge science. It is a journey that calls for cautious optimism, interdisciplinary collaboration, and a commitment to patient safety. Such a balanced, integrative strategy not only addresses the current health challenges but also paves the way for a more resilient future in the ongoing battle against antibiotic resistance in gonorrhea.
As we continue to explore and refine these innovative strategies, the lessons learned from both modern and traditional practices will serve as a valuable roadmap. The effort to merge these approaches could ultimately transform our therapeutic landscape—providing a more sustainable, clinically effective, and culturally respectful solution to one of the most persistent infectious diseases of our time.
Originally Post From https://www.frontiersin.org/journals/pharmacology/articles/10.3389/fphar.2025.1694041/full
Read more about this topic at
Chronic Gonorrhea Relief with Traditional Chinese Medicine
Effect of 13 traditional Chinese medicine drug preparations …